UT Austin launches a pioneering initiative in AI-accelerated civil engineering with a $7M NSF award

Originally published on: Geoelements news
The University of Texas at Austin is launching Chishiki.AI an innovative project supported by a $7 million grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF). Chishiki aims to revolutionize Civil and Environmental Engineering by integrating artificial intelligence. Chishiki will focus on enhancing U.S. infrastructure, developing AI-accelerated applications, and building a community of Cyber Infrastructure (CI) professionals. The project is in collaboration with the Cornell Virtual Workshop.
Transforming U.S. Infrastructure with AI
Chishiki.ai aligns with key objectives outlined in the 2020 National Artificial Intelligence Initiative Act and the 2022 Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. The project aims to strengthen U.S. infrastructure by building an integrated community of Computational Infrastructure professionals (CIPs) across AI and CEE sectors. Strategic Approaches
The Chishiki project leverages four primary strategies to cultivate a sustainable, diverse, and integrated community of CIPs:
- Promoting Collaboration: Initiatives like research summits, fellowships, joint research, and industrial partnerships encourage cooperation between CIPs and domain experts.
- AI-Powered Learning Environments: The project offers scalable, personalized learning platforms, enhancing the educational experience in CEE.
- Developing AI-Enabled CI Architectures: This includes creating efficient, reproducible workflows for CIPs.
- Fostering Diversity: By engaging with historically underrepresented institutions, the project aims to create a more inclusive CIP community.
Additionally, Chishiki provides peer mentoring and collaborates with the NSF ACCESS Computational Science Support Network (CSSN) to bolster research activities in CI and CEE.
Forging Future CIPs
The Chishiki Graduate and Undergraduate Fellowships are integral to fostering a diverse and sustainable pipeline of future CyberInfrastructure Professionals (CIPs). The Graduate Fellowship welcomes students from various academic backgrounds who are keen on CI-oriented careers and Civil and Environmental Engineering (CEE) applications. This fellowship includes a full-year stipend, allowing graduate fellows to stay at their home universities during the academic year and participate in an intensive summer residency at UT Austin. Additionally, Chishiki supports the Undergraduate Training Program for five undergraduates each summer with full stipends. We offer intensive training and independent projects to help undergraduates explore CIP career pathways, emphasizing real-world problem-solving and the development of specialized CI skills.
Educational Innovations in AI and CEE
Chishiki.ai introduces new courses for CI professionals, covering areas such as AI4CI, CI4AI, and Scientific Machine Learning. These courses delve into AI-enabled programming, AI-enhanced performance tuning of High-Performance Computing (HPC) systems, AI-driven knowledge discovery, and the development of large-scale AI systems. A notable aspect is the integration of techniques for explainable AI and differentiable programming.
Scalable Learning with AI
The project pioneers a novel learning environment using Large Language Models and reinforcement learning to create personalized educational materials. This AI tutor system will generate individualized quizzes and explanations, tailored to each learner’s unique needs and abilities. These resources will be available as open-access content on the Cornell Virtual Workshop (CVW) learning platform.
Innovative Research Directions in AI-Enhanced Civil and Environmental Engineering
The Chishiki.ai project is set to revolutionize Civil and Environmental Engineering (CEE) with the integration of AI. The project emphasizes three critical areas:
- AI-accelerated simulations: Chishiki.ai aims to drastically improve the efficiency and scale of simulations in CEE. By leveraging the Graph Network Simulator, the project can conduct full-scale fluid and soil simulations at speeds 1000 times faster than traditional methods.
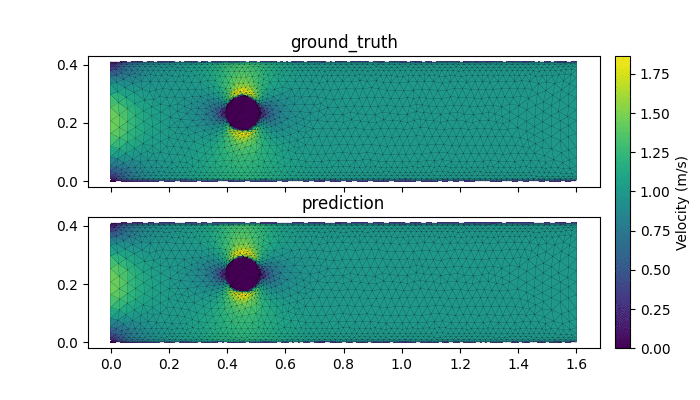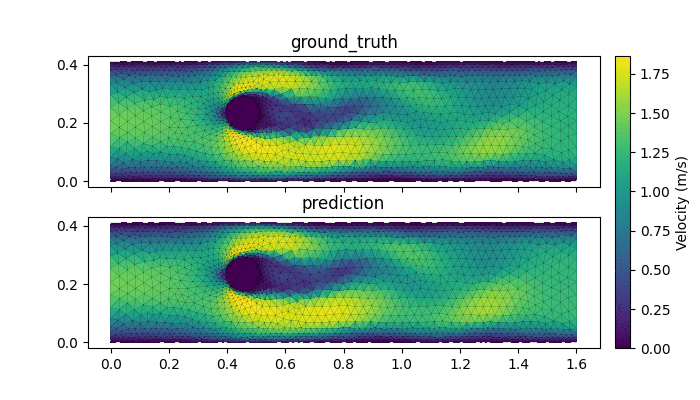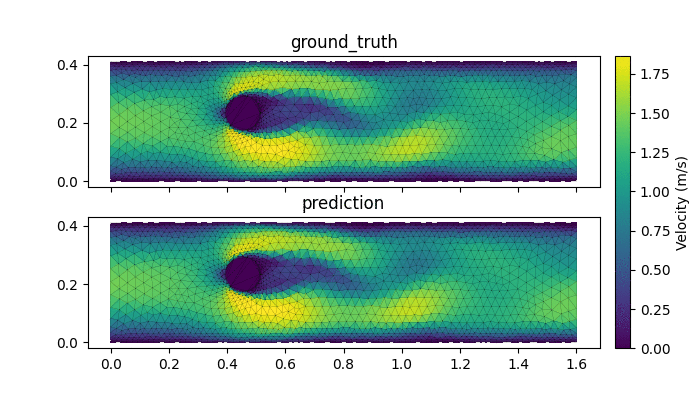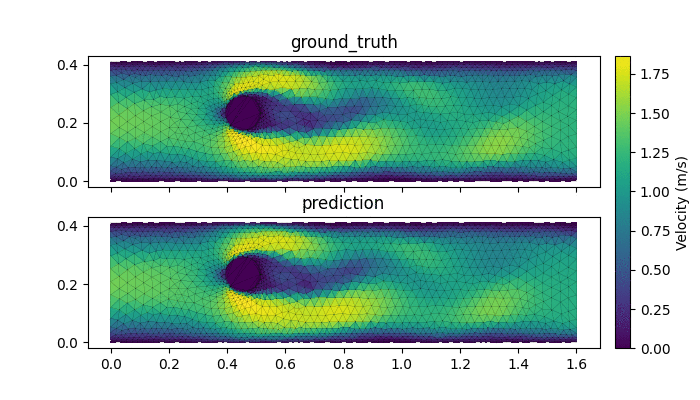
AI accelerated surrogate model with Geoelements GNS
Foundational AI Models for Structural Health Monitoring: The project is developing specialized AI models for structural health monitoring, tailored for low-resource settings such as edge devices. These models aim to provide high accuracy in real-time monitoring under various environmental conditions.
Knowledge Discovery in Natural Hazards Engineering: Chishiki.ai leverages AI to transform knowledge discovery in Natural Hazards Engineering. By creating a metadata knowledge graph from extensive datasets, the project enables complex queries and insights that were previously unfeasible.
Impact and Accessibility
With the objective to benefit over 500 CIPs nationwide and train more than 300,000 users globally through CVW, Chishiki.ai is poised to make a significant impact. The project’s deliverables will be made available on NSF-funded platforms like DesignSafe and the Texas Advanced Computing Center, ensuring broad adoption of AI-enhanced CI innovations. We plan to fully fund and support graduate and undergraduate students through the project.

This NSF award represents not just a financial investment but a commitment to advancing the field of civil engineering with AI. It’s a testament to the NSF’s ongoing mission to support projects with high intellectual merit and broad impacts, further cementing Chishiki.ai’s role in transforming the landscape of civil and environmental engineering through AI integration.
